With the latest in face recognition and other biometric technology coming to the consumer level, biometric security may begin to cross your mind. You may wonder “Is biometric actually more secure?” The short answer is that it’s stronger than using a weak password, but not as strong as using a strong password. For more info on what factors go into making a password strong, check out this excellent article about password strength.
With that being said, let’s dive further into the details.
What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is the ability to control access to a resource (devices, location, etc) based on certain biometric identifiers. Wikipedia defines biometric identifiers as “the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological versus behavioral characteristics. Physiological characteristics are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina and odor/scent. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to typing rhythm, gait, and voice. Some researchers have coined the term behavior metrics to describe the latter class of biometrics.”
Here’s a list of common methods of biometric authentication:
Fingerprint Recognition
Fingerprint recognition works by using the unique surface of your fingerprint for identification and is probably the most widely used form of biometric authentication. It’s widely used in several mobile devices. Some businesses also use this technology as part of a timeclock for a more accurate timecard.
Face Recognition
This method uses the facial features that are unique to a person to identify them. This was first used in law enforcement and security, but the recent generations of mobile devices now use face recognition to unlock the device.
Voice Recognition
Voice Recognition analyzes the frequencies of your voice to identify you. This feature recently started popping in virtual assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Apple’s Siri and Microsoft’s Cortana.
Iris Recognition
This utilizes the unique characteristics of your iris, the colorful section of your eye, to identify you. While this is used in security applications, you’re unlikely to see it at a consumer level.
How secure is biometric?
As more and more services utilize biometric data, there will be a larger collection of biometric data that could potentially be vulnerable to attack. Some of these places may or may not use the same level of security that large companies like Google & Apple employ. It’s almost inevitable that throughout some point, the data will eventually be compromised.
This brings up the real “issue” with biometric security. If it was a password that was compromised, you could simply change the password to an infinite number of other passwords. With biometric security, you can’t change your retina or fingerprint. On top of that, a skilled attacker could take a high-resolution photo of the fingerprints from a glass from a restaurant or coffee shop to duplicate the biometric data.
Currently, laws and legislations regarding biometric data & privacy laws vary by region/state. According to The National Law Review, “The biometric bandwagon keeps rolling along as more and more states seek to regulate the collection, use, and retention of biometric data. Currently, three states, Illinois, Texas, and Washington, have biometric privacy laws in place, while the California Consumer Privacy Act (“CCPA”), goes into effect on January 1, 2020. Now, on the heels of a seminal decision addressing the Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (“Illinois BIPA”), which we recently discussed, Arizona, Florida, and Massachusetts have become the latest states to propose legislation addressing the issue of biometric privacy, and other states are also considering biometric privacy laws.”
How I can help?
Opt-out when not needed
By default, Facebook will scan photos and use facial recognition in photos and videos. In Facebook, you can disable this option by going to Settings > Face Recognition. This will display a screen like below:
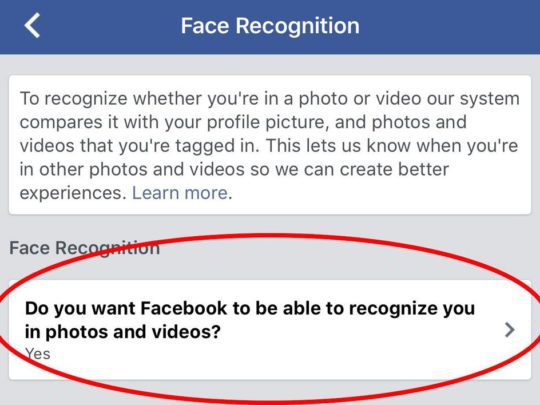
This will prevent Facebook from using your profile picture to scan other photos in an attempt to recognize you in other photos.
Strong passwords
As mentioned above, biometrics are stronger than using a weak password, but not as strong as using a strong password. For an excellent article on making a strong password, check out this excellent article about password strength. Stronger passwords will do a few things to help out. They can take the place of using biometric authentication and they can also keep your accounts safe that store information, including your biometric information.
Keep all software up to date
While this seems like an odd tip, it’s a useful one. By keeping all of your software up to date, you’re eliminating one of common attack methods to allow your data to be compromised: Software Vulnerabilities. For a more in-depth article on this topic, please check out “Why is Patch Management Important for Cyber Security?“.
Hopefully, this sheds some light on the good & bad of biometric security. If you ever have any questions about cybersecurity or any other type of technology question, feel free to call the experts at SandStorm IT at 901-475-0275.

